Every year, Metabase Q conducts numerous assessments on Point of Sale (PoS) devices across LATAM.
These assessments play a crucial role in strengthening companies’ devices before they hit the market. Through these evaluations, the Ocelot Offensive team has identified a prevalent trend: approximately 90% of PoS devices integrate Bluetooth chips sourced from Yichip, a Chinese manufacturer known as Yizhao Microelectronics (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd. Notably, Yichip extends its support to various IoT devices, as detailed on their official website at http://www.yichip.com/yc10XX
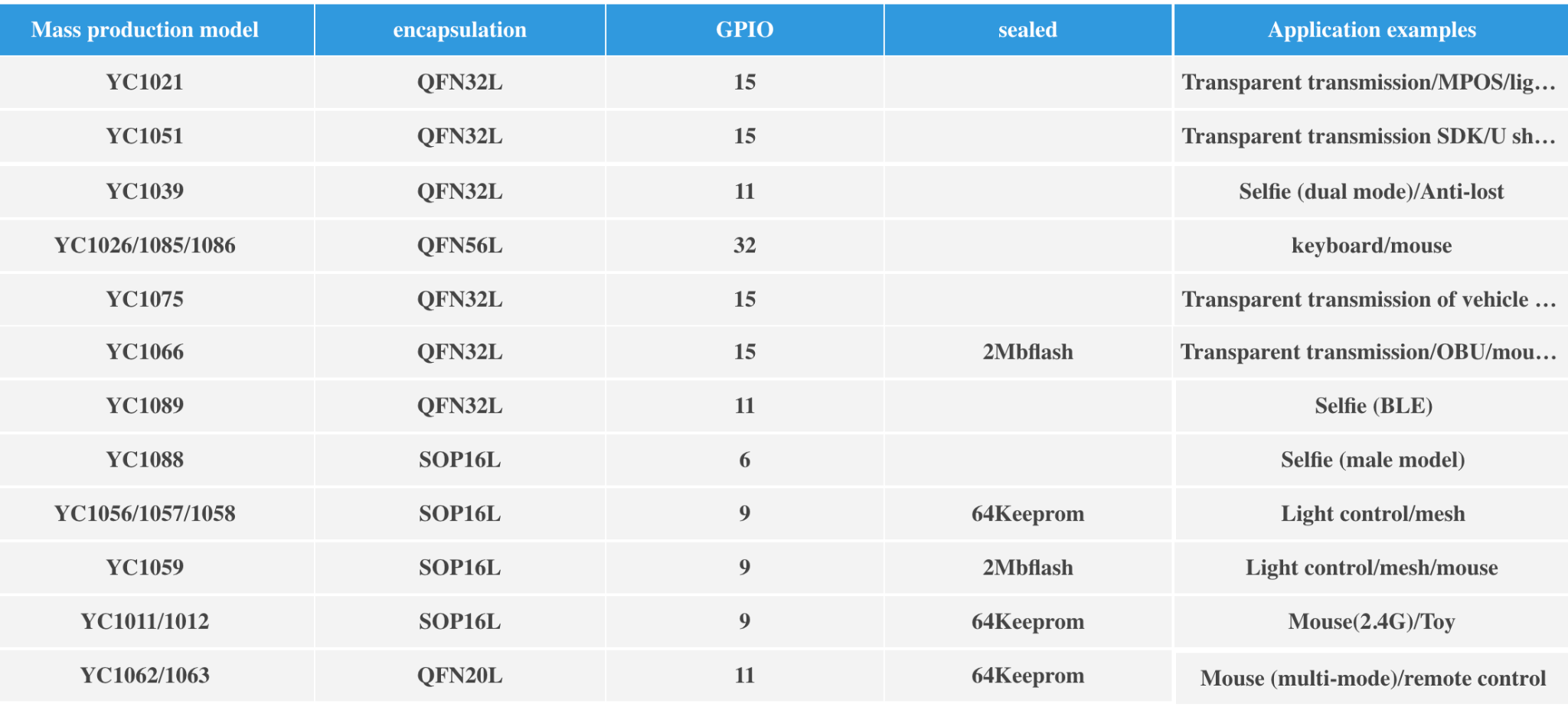
The affected Bluetooth chip belongs to the YC10XX series, described by the manufacturer as the leading chip within the financial sector. This assertion seems accurate, given that one out of two Point of Sale (PoS) devices tested in LATAM incorporates this chip.

In this brief blog post, our goal is to inform the community about two high-severity bugs we have uncovered. These vulnerabilities have the potential to enable attackers to execute:
- Unauthenticated Remote Memory Leak
- Unauthenticated Remote Device Crash
As responsible disclosure is crucial, we refrain from providing proof of concept, as these vulnerabilities remain unpatched globally.
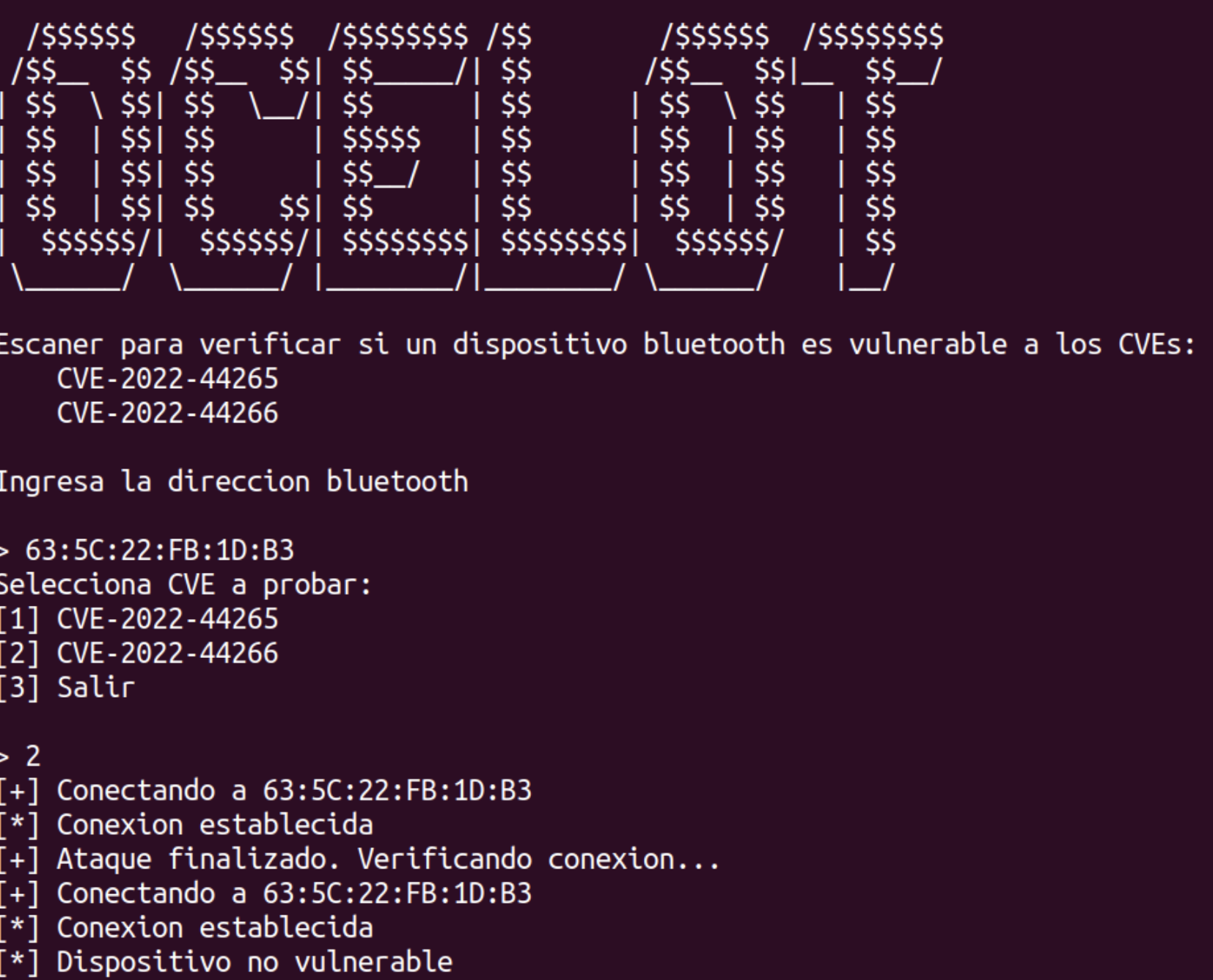
Lastly, the Ocelot team has developed a free tool to test if a PoS device is vulnerable. Feel free to reach out to us for assistance in testing your device at: https://www.metabaseq.com/contact-us/
Disclosure Timeline:
- May 4th, 2022, June 25th, 2022 – Vulnerabilities found
- July 4th, 2022: Vulnerabilities reported to Yichip via email
- No response after a couple of attempts
- Jan 4, 2023: MITRE assigned CVEs for the vulnerabilities
MITRE has reserved a couple of CVEs for these issues, described in the next section.
CVE-2022-44265: Remote Bluetooth Yichip memory leak
- Severity: High
- Device: Multiple MPOS-based
- Discovery date: May 4th, 2022
- Affected component: Yichip Bluetooth Stack – YC1021
- Vulnerability type: Remote Info Leak
Vulnerability Description
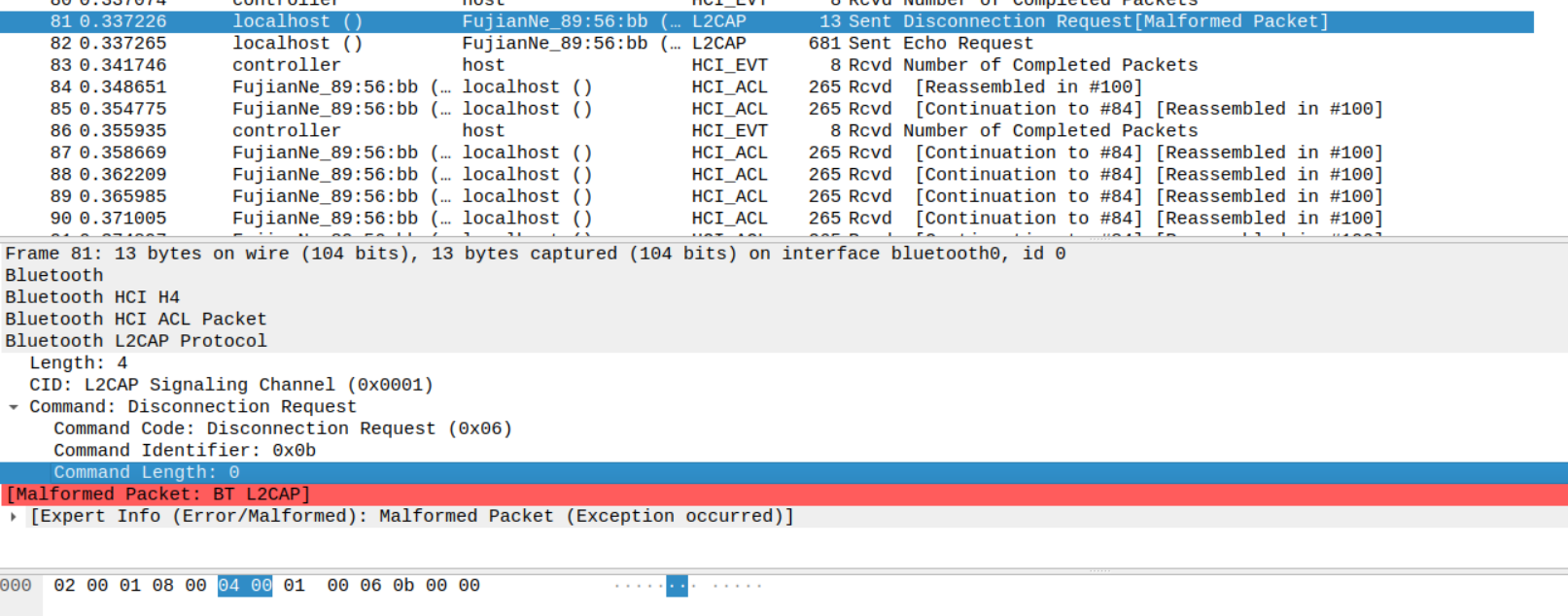
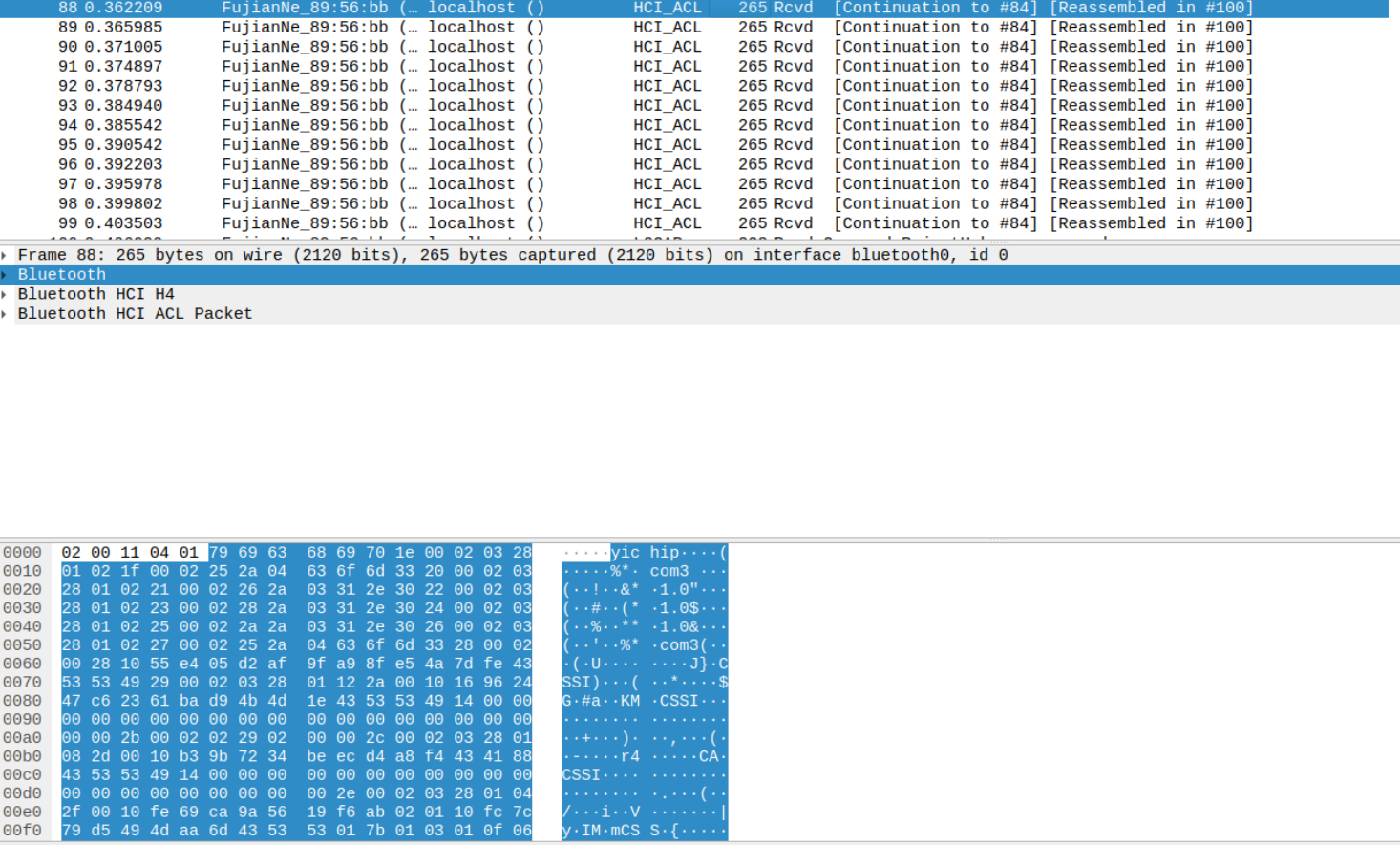
An attacker in the Bluetooth range of a PoS/IoT device using Yichip YC1021, can send it a malformed L2CAP command and the PoS sends back the dump from a page of memory (4kB) which could leak sensitive information.
Evidence
Request:
Response from Device:
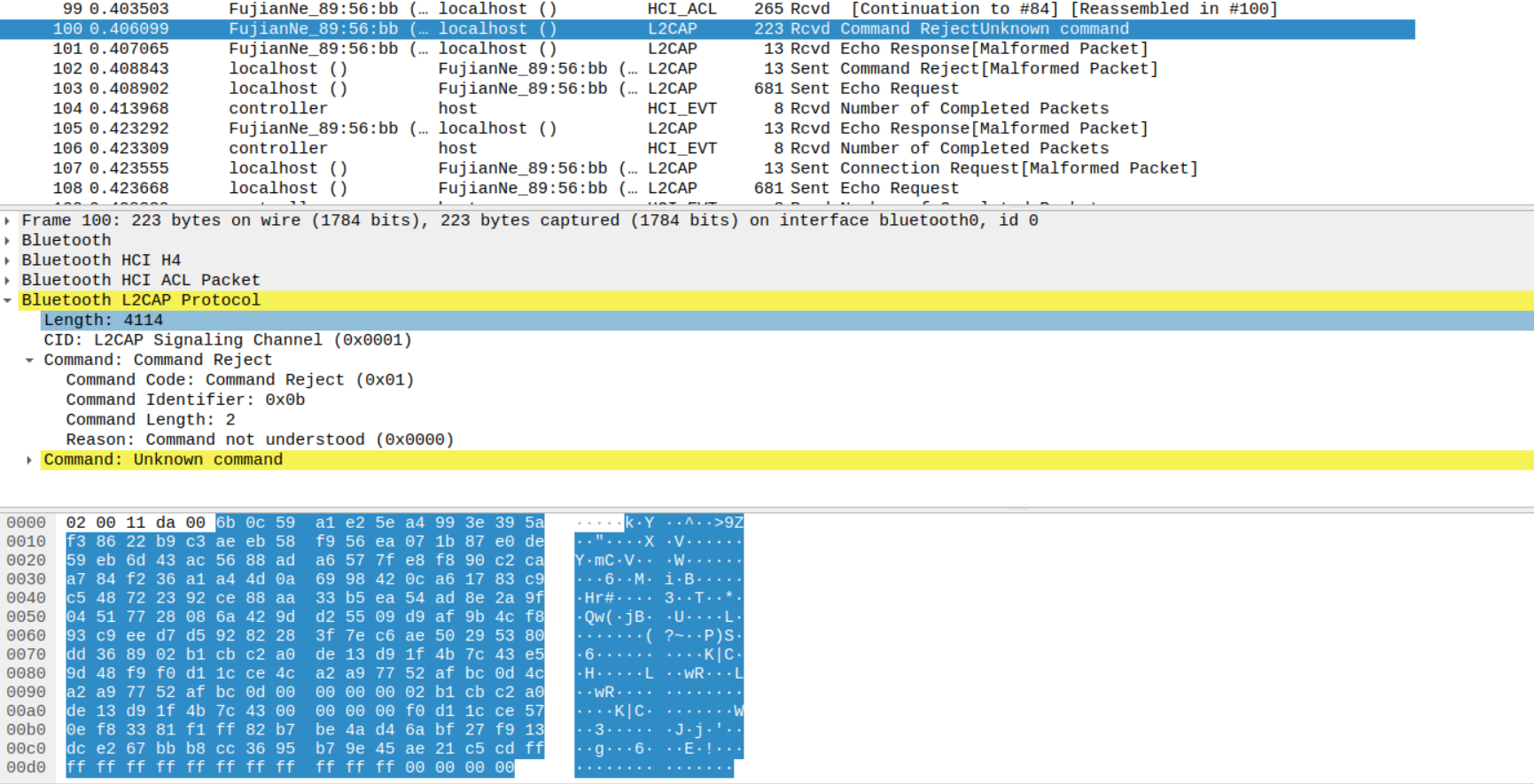
CVE-2022-44266: Yichip Bluetooth Stack Crash
- Severity: High
- Device: Multiple MPOS-based
- Discovery date: June 25th, 2022
- Affected component: Yichip Bluetooth Stack – YC1021
- Vulnerability type: Remote Crash
Vulnerability Description
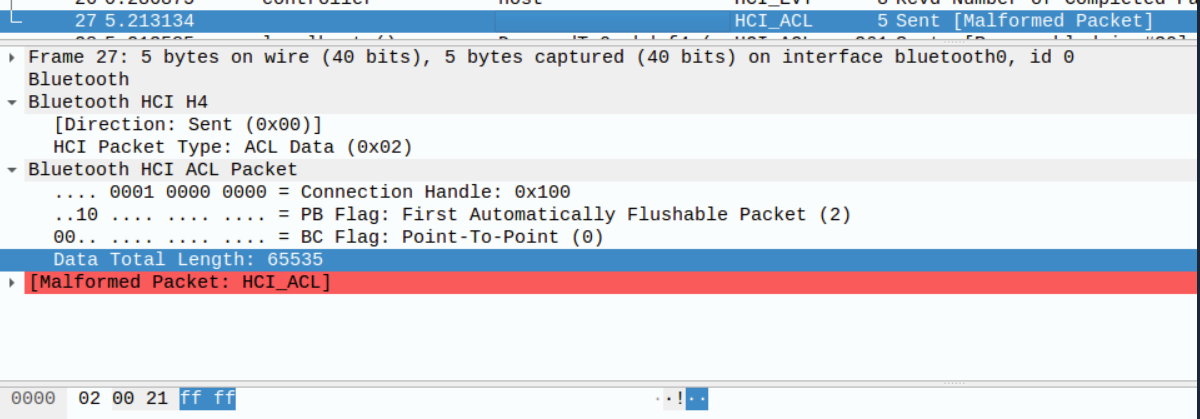
An attacker in the Bluetooth range of a PoS/IoT device using Yichip YC1021, can send it a malformed ACL package specifying a fake considerable length (0xffff). This manipulation results in a Bluetooth stack crash, causing the device to cease responding to Bluetooth connections until a manual reboot is executed.
Evidence
Sending package: We launch the attack sending one l2cap_echo cmd, then the malicious payload:
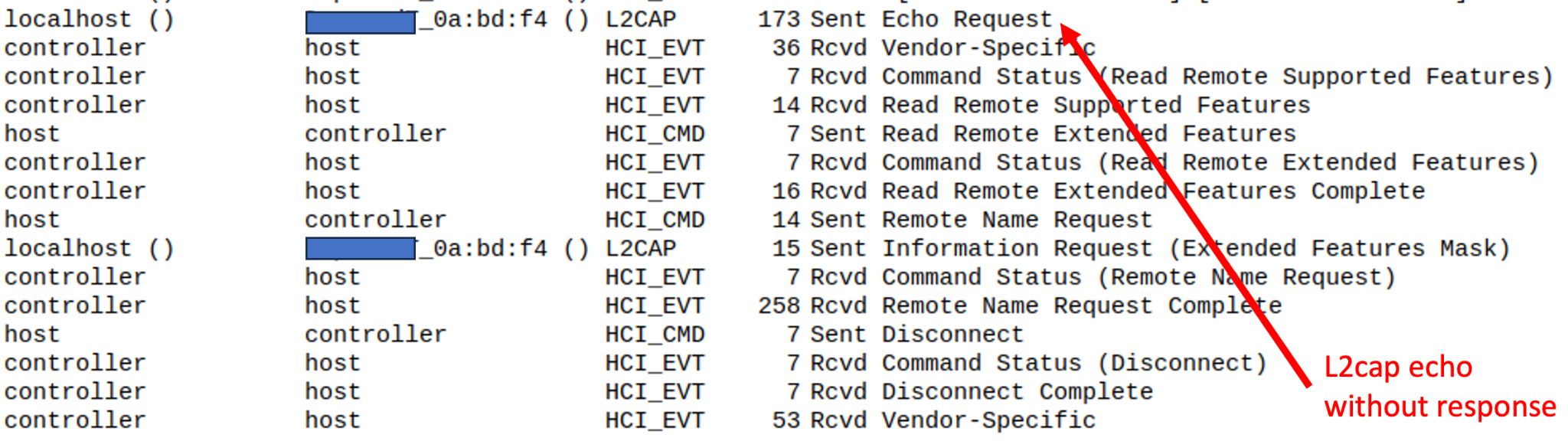
Then, to confirm the device Bluetooth stack is down, we sent a l2cap_echo without getting any response, confirming the crash:
Conclusions
Point of Sale and IoT devices are an entry point to organizations and hold sensitive data that, if leaked, could even lead to a PCI Violation. Custom hardware and software are required to test Bluetooth and NFC stacks in order to find high-severity bugs. We recommend undergoing security checks early in the release process, as fixing bugs in production can be extremely expensive for companies!
Our innovative tools empower us to conduct in-depth device testing, exploring the deepest levels of protocols. Get in touch with us today!

